Node class
Node is the basic signal processing unit in collar.js
Collar.js is based on bouton.js, a reactive library. Each node supports bi-directional data flow:
- from upstream to downstream, usually this is used to handle data
- from downstream to upstream, usually this is used to support back pressure
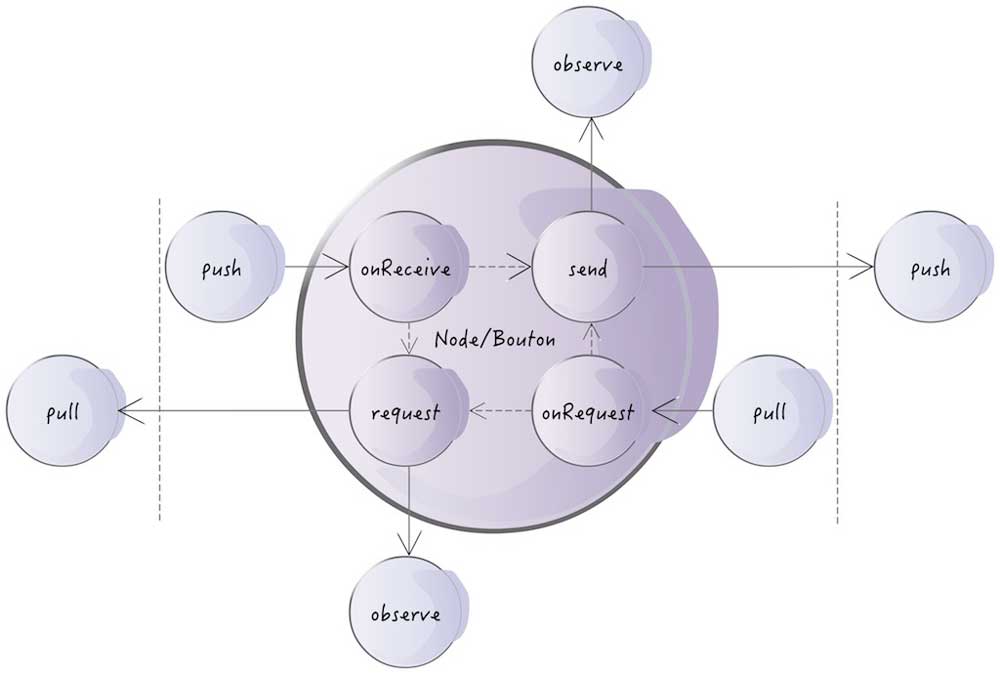
It has four basic methods:
From upstream to downstream
- push(data): pass data to the node, and start processing it
- send(data): emit a signal with the data as payload and pass it to all downstream nodes
From downstream to upstream
- pull(cmd): pass a command to the node, and start processing it
- request(cmd): request the cmd to its upstream nodes.
constructor(options, eventemitter)
Create a new node
Arguments
| Arguement | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| options | map | the options |
| eventemitter | EventEmitter | the event emitter used in the node |
Return
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Node | the node |
Node.push(data, interruptible)
Push a data to a node for processing. By default, when one node finished processing the signal, collar.js will release the cpu and give other node a chance to run and processing other signals. Sometimes, you want the current signal to be processed without any interruption, this is done by pass a false as the second argument.
Arguments
| Arguement | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| data | any/Signal | the data or a signal containing the data |
| interruptible | boolean | optional, if the signal processing can be interrupted during propagation, default true |
Return
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Node | the node |
push a signal to node
const ns = collar.ns('test');
const doubleNode = ns.map(s => {
return s.new({
v: s.get('v') * 2
})
});
doubleNode
.do('log', s => {
console.log(s.payload); // --> 20
});
doubleNode.push({v: 10});
Node.send(data, interruptible)
send a data from current node to all connected downstream nodes. By default, when one node finished processing the signal, collar.js will release the cpu and give other node a chance to run and processing other signals. Sometimes, you want the current signal to be processed without any interruption, this is done by pass a false as the second argument.
Arguments
| Arguement | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| data | any/Signal | the data or a signal containing the data |
| interruptible | boolean | optional, if the signal processing can be interrupted during propagation, default true |
Return
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Node | the node |
push a signal to node
const ns = collar.ns('test');
const doubleNode = ns.map(s => {
return s.new({
v: s.get('v') * 2
});
});
doubleNode
.do('log', s => {
console.log(s.payload); // --> 10
});
// this data will not be processed by doubleNode, it is emitted by doubleNode and pipe to connected downstream node
doubleNode.send({v: 10});
Node.to(comment, node)
Connect current node to another node
Arguments
| Arguement | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| comment | String | optional, the comment |
| node | Node | the downstream node |
Return
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Node | the downstream node |
push a signal to node
const ns = collar.ns('test');
const doubleNode = ns.map(s => {
return s.new({
v: s.get('v') * 2
});
});
const logNode = ns.do(s => {
console.log(s.payload);
});
doubleNode.to(logNode);
doubleNode.push({v: 10});
// console output: {v: 20}
Node.through(comment, inputNode, outputNode, asActuator)
Pass signal to a pipeline, from the inputNode, to outputNode, and send the result signal to downstream node
Arguments
| Arguement | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| comment | String | optional, the comment |
| inputNode | Node | the input node of the pipeline |
| outputNode | Node | optional, the output node of the pipeline |
| asActuator | boolean | optional, is the pipeline behaves as an actuator or a processor, default: false |
Return
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Node | the delegator node or output node |
const ns = collar.ns('test');
const input = ns.input('pipeline input');
const output = ns.output('pipeline output');
const doubleNode = ns.map(s => {
return s.new({
v: s.get('v') * 2
});
});
input.to(doubleNode).to(output);
const input2 = ns.input('pipeline 2 input');
const input3 = ns.input('pipeline 3 input');
input2.through(input, output) // as a processor, output signal pipe to downstream directly
.do(s => console.log('as processor: ', s.payload));
input2.push({v: 10});
// console output --> as processor: {v: 20}
input3.through(input, output, true) // as an actuator, output signal payload stored in __result__ field
.do(s => console.log('as actuator: ', s.payload));
input2.push({v: 10});
// console output --> as actuator: {v: 10, __result__: {v: 20}}