Advanced Usage
Usually, all you need is to use the architecture API to write your application. See the following predefined architectures:
However, sometimes you probably want to create a customized data flow. In this chapter, I will introduce how to create a customized data flow with collar.js
Reimplement a reducer data flow with collar.js
Collux is based on collar.js. The predefined architecture is just a shortcut to build data flow. Under the hood, the architecture API (for example, app.reduce) uses collar.js API to build the data flow.
Let's review the single route app data flow:
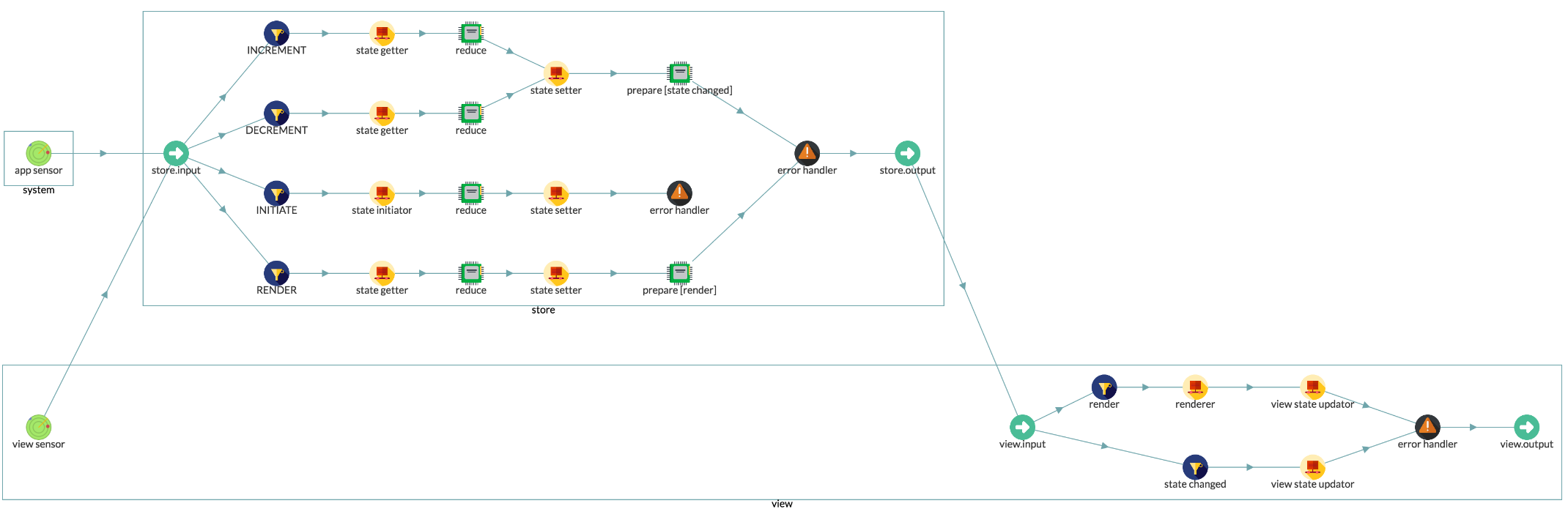
A reducer data flow look like this:
store input
-> action filter -> get current state
-> reducer -> save state to store -> prepare [state changed] msg
-> store output
You need to use collar.js API to create each node and connect them together.
We can get the store input and store output from the store component:
const input = app.store.input();
const output = app.store.output();
Next, we can implement the 'INCREMENT' data flow as following:
var state = 100; // this is the current state object
input
.when('INCREMENT', s => s.get('actionType') === 'INCREMENT')
.do('get current state', s => {
return state;
})
.map('reduce', s => {
let prevState = s.getResult(); // get the result from previous actuator ('do' operator)
return s.new({ // return a new signal
state: prevState + 1
})
})
.do('save new state', s => {
state = s.get('state'); // save the state to local store
})
.map('prepare a state changed msg', s => {
return s.new({
msgType: 'state changed',
state: s.get('state')
})
})
.to(output); // pipe it to the output
If you want to customize the action, you can wrap the flow in a function, and pass an action type string and a reducer function to it, so that each time you call the function, it generate a new data flow with new action type and reducer.
function createReducerDataflow(actionName, reducer) {
input
.when(actionName, s => s.get('actionType') === actionName)
...
.map('reduce', s => {
let prevState = s.getResult();
let newState = reducer(prevState, s.payload); // signal payload is the action object
return s.new({ // return a new signal
state: newState
})
})
...
.to(output);
}