ReduxMultipleRoutesApp
In multipls routes redux application, there are four components:
- store component
- router component
- view component
- system component
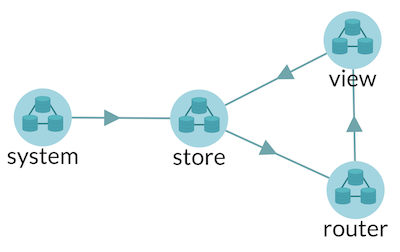
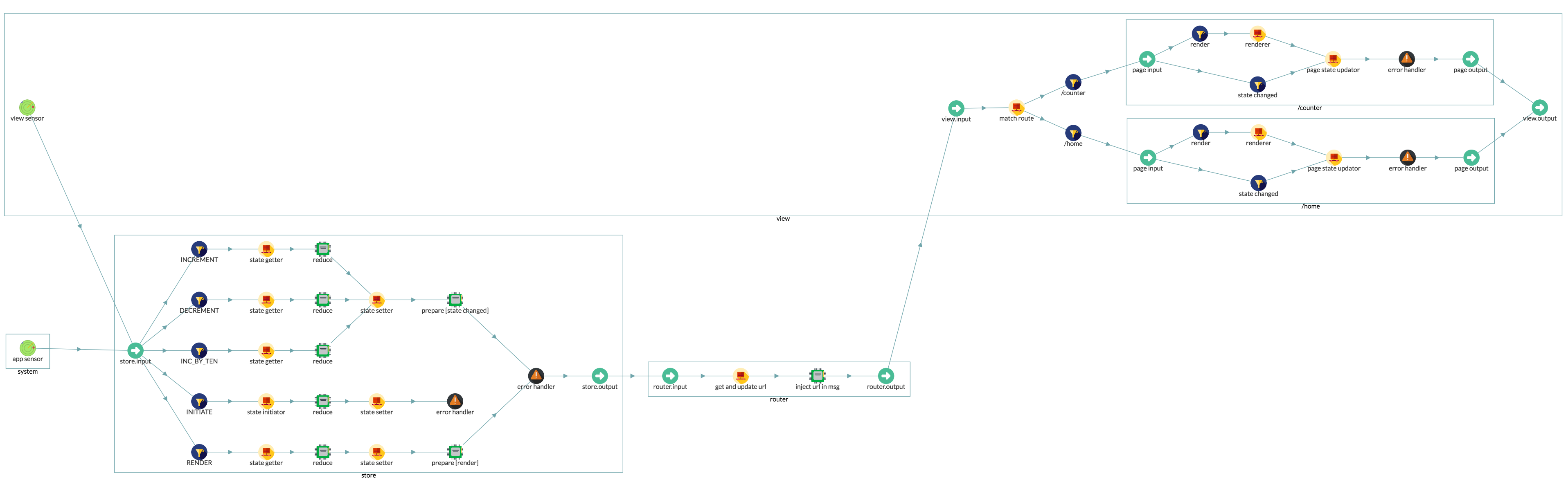
See the following diagram to understand the architecture and data flow of redux multiple routes application architecture. (This diagram is generated from collar dev tool)
Check ReduxMultipleRoutesApp class
Architecture Guide
The multiple routes application architecture can be customized in the following ways:
Setup the initial state
This could be done either by the constructor option initState, or through the setStoreStateInitiator function.
const app = Collux.createApp('redux-single-route-app', {
initState: () => {
return 100;
}
});
Or
app.setStoreStateInitiator(() => {
return 100;
})
Add a route
You need to specify two options (render and updateState) to add a page to the application.
var counterView = null;
app.route('/counter', {
render: () => {
counterView = ReactDOM.render(
<CounterView />,
document.getElementById('counter')
)
},
updateState: (state) => {
counterView.setState({
value: state
})
}
})
Set the default route
By default, the default route is '/'. You can change the default route with setDefaultRoute function
app.setDefaultRoute('/counter');
Set the root path
If your application starts from a path different from '/', you can call setRootPath(path) method to setup the root path
app.setRootPath('/example');
Use middleware
Middleware is used to manipulate the message sent from store to view component. A middleware is a function, which takes message as input and output a message to next middleware or view:
app.use('log middleware', msg => {
console.log(msg);
return msg;
});
The default multiple routes app architecture integrates a router middleware.
Add reducer to handle actions
You can use reduce function to add a new action processing data flow, for example, the INCREMENT action data flow in the above diagram is created by the following code:
app.reduce('INCREMENT', (prevState, action) => {
return prevState + 1;
});